The Channel Letter Return (CLR) Plots feature enables you to easily and quickly generate plots that help in creating channel letter returns.
Simply select the text used for the signage, select Channel Letter Returns in the Tools Menu, and the dialog box below will appear. The text must be Combined into one object prior to entering the tool.
Below is a description of the six primary settings in the dialog box:
Offset
Enter the offset amount to apply around the shape. This is typically the thickness of the material (e.g. 0.040") which insures that the letter back will fit properly inside the completed return. You must create the offset before the OK button will be available. See below for instructions on creating reverse/halo lit return patterns.
Tool Diameter
This number tells the software how much to compensate for the tool diameter on all left-hand turns in the cutting path, where the tool's diameter prevents sharp corners from being created. Enter the diameter of your router bit in this box. If you are cutting your bakcs with a laser, then you can enter 0 here. The image below shows what this option does:
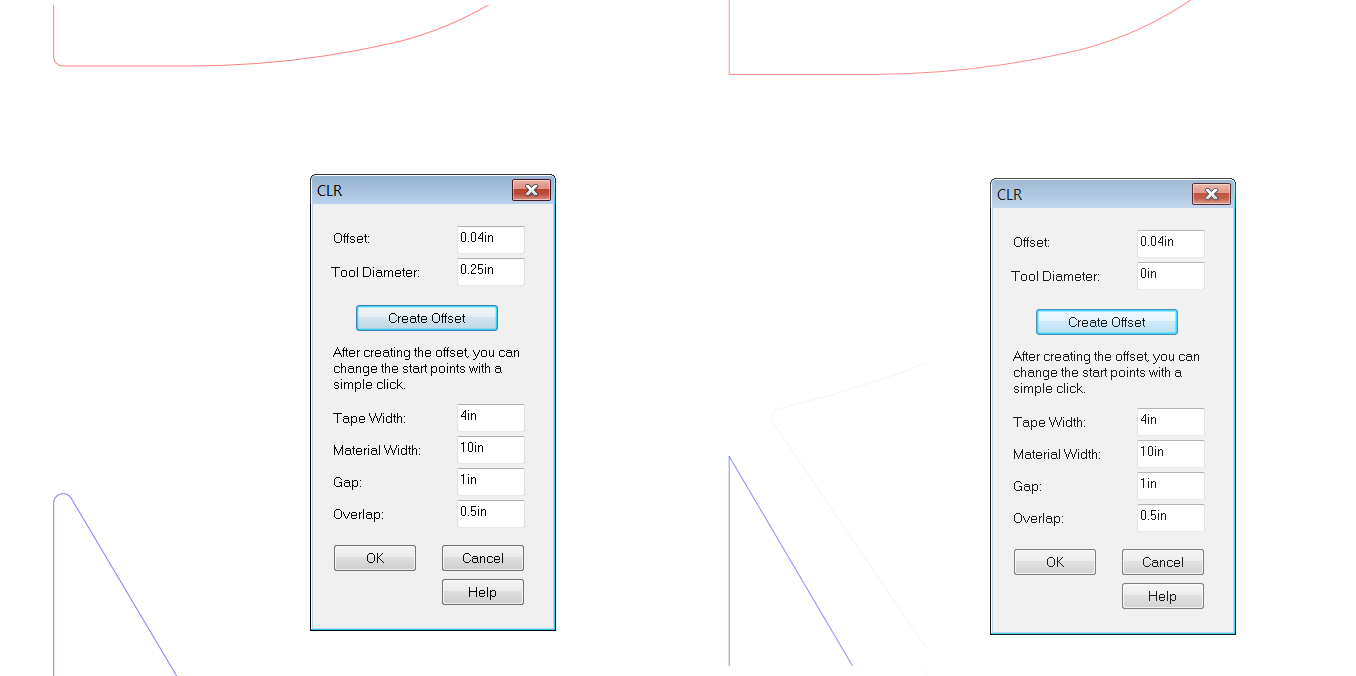
The image on the left shows the radius on these inside corners, with a 0.25" Tool Diameter. The image on the right shows a 0.00" Tool Diameter and sharp inside corners.
Create Offset
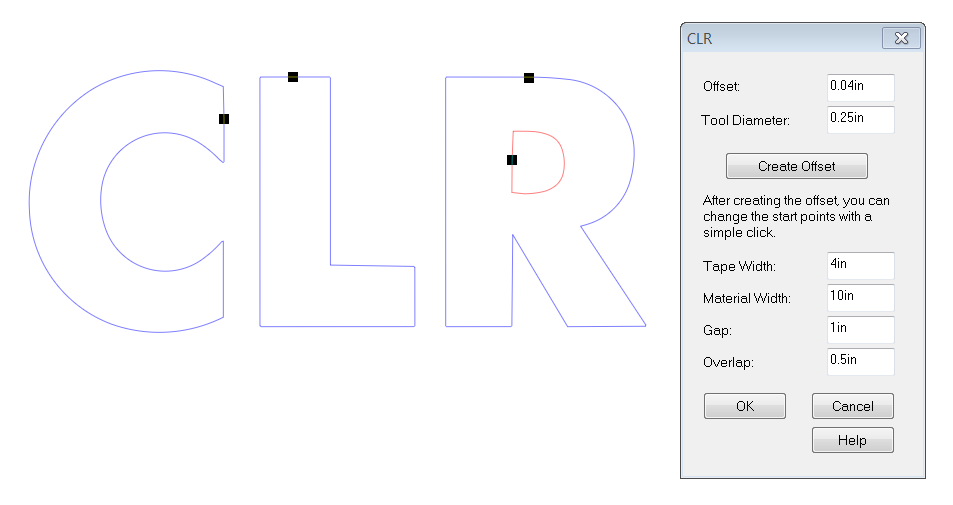
After you have entered these two values, click on Create Offset prior to moving onto the additional options. As it says below the button, "After creating the offset, you can change the start points with a simple click."
The Start Points are where each pattern starts and ends, and therefore where you have to clinch the ends of the return together. Most shops will put these along the tops of the letters, but you can move these points anywhere (such as a vertical or a straight line) by just clicking at this stage in the process. Note that the internal loop gets its own pattern.
Tape Width
Enter the width to be used to create the channel letter return patterns. This can be as wide as the return strip (e.g. 4") or smaller if you prefer (e.g. 2"). This width should not to be confused with the width of plotting material, below.
Material Width
Enter the net plotting width of the material in the plotter. If you are using a 24" wide material in a plotter designed to use 36" material, the net plotting width should be 22" (24"-2" to allow for the non-plottable material on each edge). The non-plottable allowance varies from plotter to plotter, but 2" is a safe amount that will work with most plotters. The patterns will be stacked to the width value.
Gap
Enter the gap between individual tape loops. This covers both the horizontal and vertical gap. This is typically 1/2" (0.5"), enough to cut the loops apart with scissors or a razor blade.
Overlap
This is the amount for each pattern to overlap so that it can be clinched. You can enter 0 here for no overlap, but a common value would be .5"-1".
After you press OK, the pattern will be created:
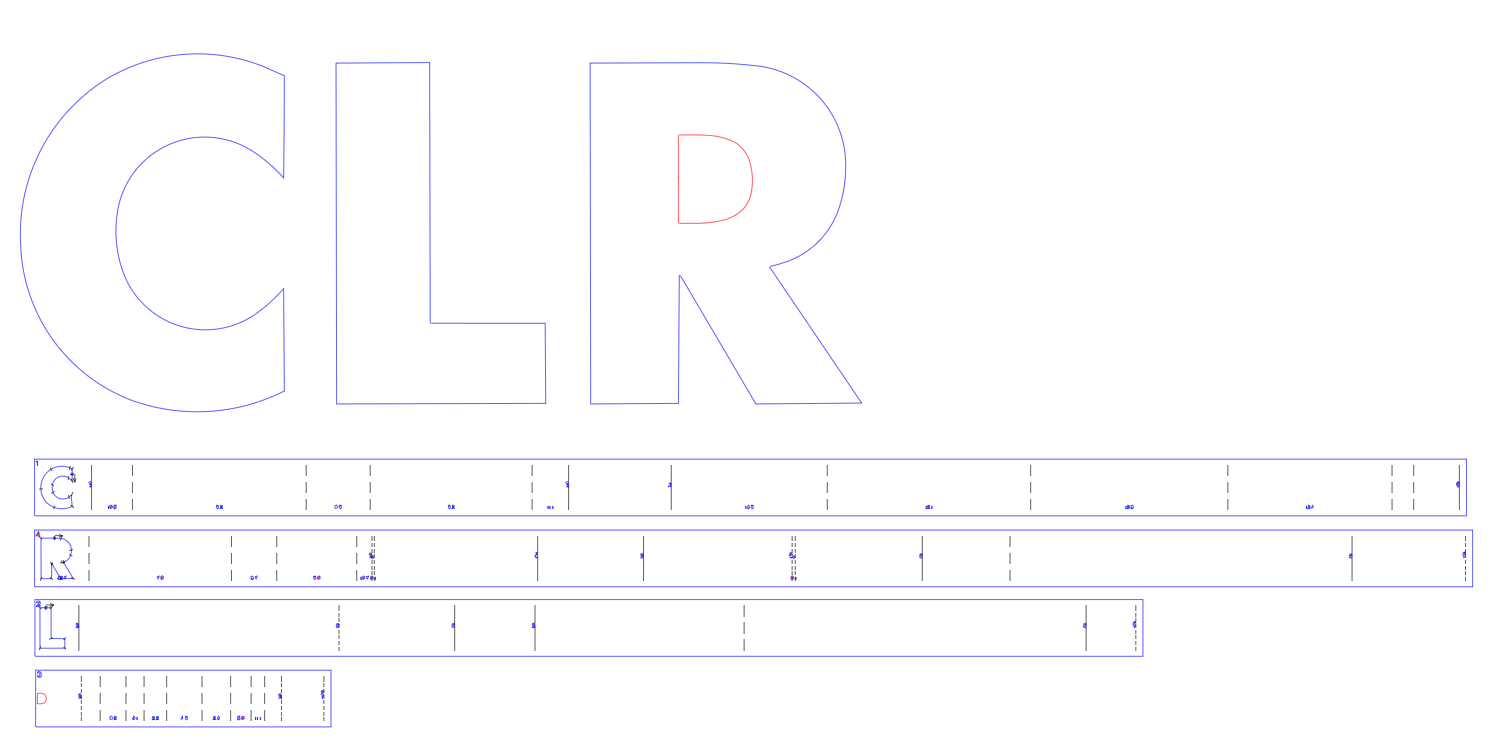
Information in the CLR plots
Several things are included in the CLR plots.
Each section (rectangle) in the CLR plot represents a "closed loop" that makes up each return. The number in the upper left corner of each section is the number of that loop, where the numbering starts with the first character on the left. If a character has one or more internal loops, the internal loops are numbered before the outer loop. For example, if the copy reads CHANNEL LETTER RETURNS, the internal loop in the A would be numbered loop 3 and the outer loop for the A would be loop 4.
At the left end of each pattern is a reduced scale image of each loop. All those images are in proportion to each other, but they are all less than full size.
The total length of each pattern will exactly match the perimeter of each letter, plus any Overlap value that you entered.
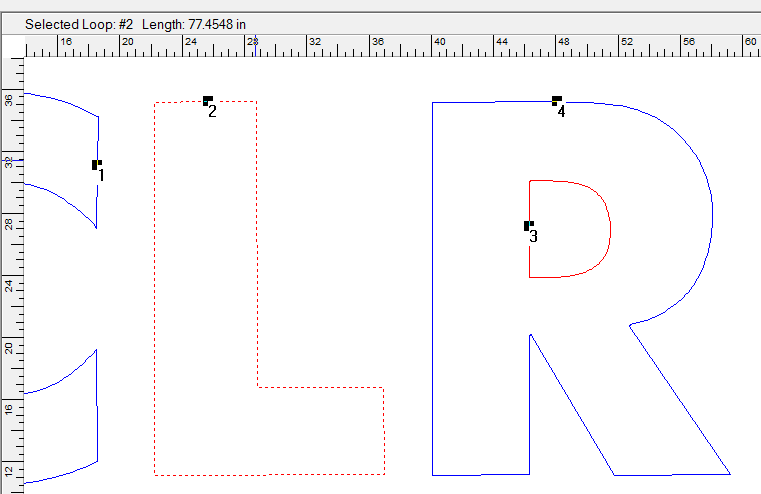
Here is the overall loop length of the "L" as shown in the Loop Edit Tool.
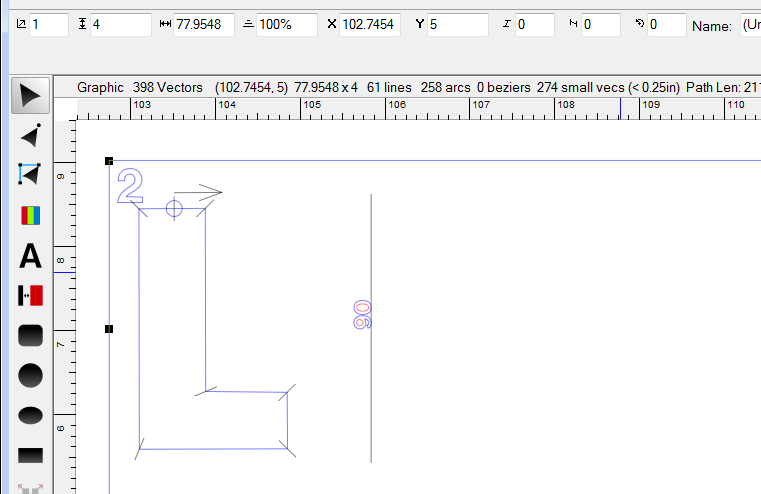
And here is the return pattern, 4" in height and the same length to four decimal places, plus the 0.5" overlap value.
There are three "line types" in the plot: (1) solid lines that indicate sharp bends in the same direction as the return, (2) short dashed lines that indicate sharp bends in the opposite from the return, and (3) long dashed lines that indicate smooth transitions between two curves or between a line and a curve.
The numbers along the bottom edge of the plot are the radii of the arcs. These numbers can be used to select the best notching tool for each arc (i.e. smaller notch angle for shorter radii and larger notch angle for longer radii).
The numbers next to a solid line (sharp bends) indicate the angle of the bend, most commonly 90 degrees.
Some shops will focus on the hard bends as the key data in the pattern, but it all depends on your workflow and equipment as to how to best interpret the pattern.
Automatic Nesting
When the patterns are created and displayed in the layout window, they have been automatically nested to optimize the use of the material. The Tape Width, Material Width and Gap settings used in the dialog box (shown above) can be adjusted to reduce the amount of plotting material needed to a minimum. For example, if you can get by with a Tape Width of 2" instead of 4", the total amount of plotting material required would be reduced by 50%.
Output
There are various options for output of the patterns, the most common being plotting to paper. Note that LED Wizard does not have a plotting option, so you would export the pattern to a vector file such as DXF. You can also consider printing the patterns to a large format printer, either to paper or adhesive backed vinyl. Some shops even export the pattern and then etch the markings directly on a sheet and sheer off the returns. Or you could laser cut, water jet, or plasma cut.
If you plot the patterns, be very careful about yor paper tracking long lengths. Some of these patterns are very long. Although not in style anymore in the industry, a classic 12" plotter with sproketed rollers and paper is a great piece of hardware to use for this application!
Reverse/Halo Lit Letters
The Channel Letter Return Plots feature is designed for traditional face lit letters, but it can be used with reverse/halo lit letters as well. In this case, you want the return to be attached to the sign face, but behind the face and not around the outside, like the letter backs. The is a subtle but critical difference.
The cleanest way to do this is take your artwork and do a negative offset (inline, negative value) of the return thickness amount (say 0.040") prior to entering the Channel Letter Return Tool. Use the square corner option in the [[Outline]] tool. Then run the tool using the same directions above, but with 0 as the material thickness, as we have already accounted for that. To be sure, the difference is small in an absolute sense, just over 1/8" on the overall length for the "L" we have been using in our example. However, 1/8" could be a pretty large amount as a gap or slop.
 LED Wizard 8 Documentation
LED Wizard 8 Documentation
 LED Wizard 8 Documentation
LED Wizard 8 Documentation